Whether you're a beginner in aluminium extrusion or an experienced extrusion designer, understanding how extrusiondies are designed to create different profile shapes and how these differences impact die manufacturing costs iscrucial.

What is an extrusion die?
An extrusion die is essentially a thick, circular steel plate with one or more openings used to form the desiredshape. They are typically made from H-13 tool steel and heat-treated to withstand the pressure and heat generatedwhen hot aluminium passes through the die.
Aluminium may seem soft, but in reality, enormous pressure is required to push a solid aluminium billet through athin, porous die to create the desired shape.
For example, pushing an aluminium billet through an 8-inch (about 20 cm) press requires a force of 100,000-125,000psi.
To put this into perspective, a high-pressure car wash nozzle sprays water at around 2,500 psi, and increasing thepressure to 5,000 psi can destroy bricks on a building.

Die profile categories
While aluminium extrusion can create many shapes, the dies used are divided into three categories: solid dies,semi-hollow dies, and hollow dies.
Solid dies
Solid dies are used to create final shapes without enclosed voids or openings, such as rods, beams, orangles. As a result, the manufacturing cost of solid dies is typically lower than that of other types ofdies.
Contact us now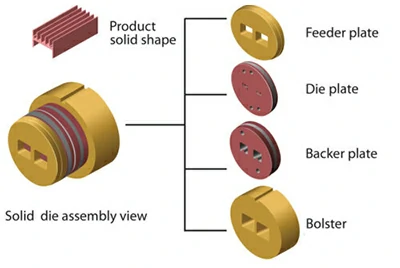
Hollow dies
Hollow dies are used to produce profiles with one or more voids, such as simple tubes with a single void orcomplex profiles with multiple fine voids.
Contact us now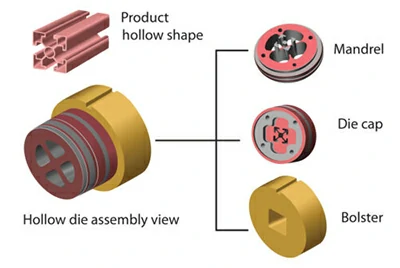
Due to the additional components, hollow dies have higher material and die costs, and generally, the more voidsthere are, the higher the cost.
Semi-hollow dies
Semi-hollow dies create profiles that are close to being hollow, with partially enclosed voids.
Contact us now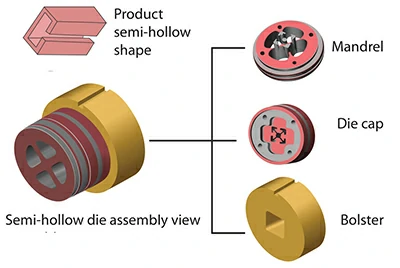
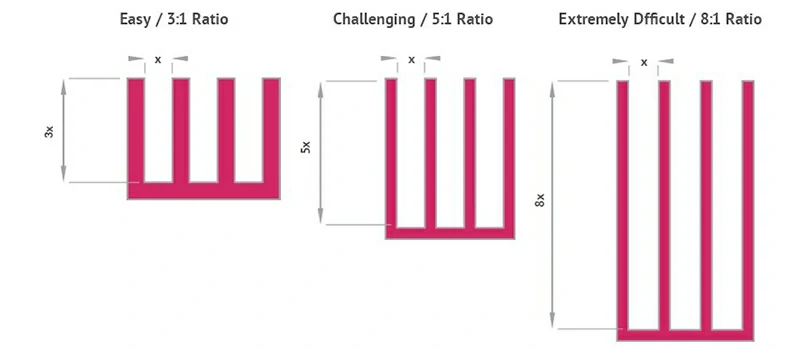
Tongue ratio example
Solid dies may also have partially enclosed voids, but the difference lies in the ratio between the void area andthe gap at the connection between the tongue and the die body. This ratio is called the tongue ratio.
The tongue ratio of semi-hollow dies is higher than that of solid dies, which increases the manufacturing complexityand, consequently, the cost.
Support tools
Dies require heavy-duty support tools to ensure proper alignment and safety during processing. Key support toolsinclude the die ring, backing plate, spacer plate, and auxiliary spacer plate.
- Die ring: Encases the die head, providing support and alignment to ensure the die head stays in the correctposition during extrusion.
- Backing plate: Reinforces the die, resisting billet pressure, and is typically two to three times thicker thanthe die.
- Spacer plate: Provides support, alignment, and even pressure distribution.
- Auxiliary spacer plate: Used when the die set is too short, extending the die set length to meet therequirements.
Stamping dies
The aluminium extrusion process relies on pressure tools to control temperature and push aluminium through the die.
Key press die components include the mandrel, extrusion block, container, liner, die slider, and horseshoe.
- Mandrel: Extends the movement range of the stamping tool and helps move the billet.
- Extrusion block: Protects the mandrel and evenly distributes pressure.
- Container: Maintains the optimal temperature of the aluminium billet.
- Container liner: Reduces wear and enhances performance.
- Die slider: Supports the press and ensures alignment.
- Horseshoe: Fixes and aligns the die ring.
Proper tool design and maintenance are crucial for optimizing extrusion performance and minimizing downtime.
Aluminium extrusion die design
Effective die design is a key aspect of the aluminium extrusion process as it directly impacts quality, efficiency,and cost-effectiveness.
In practice, the design process heavily relies on the designer's experience and intuition. However, designers alwaysconsider several key principles and techniques in each die design.
- Ensuring uniform material flow is crucial to maintain extrusion quality and die life.
- To reduce defects such as turbulence and warping, material flow can be optimized by adjusting die bearinglength, die surface length, and flow channel design.
- Longer bearing lengths are suitable for thicker areas to slow down the flow rate, ensuring that both thick andthin areas flow synchronously.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) can simulate the extrusion process and help identify potential issues in advance.
- Thermal management is critical; the die should have cooling and heating systems to maintain stable temperaturesand prevent defects caused by temperature fluctuations.
- Surface engineering, such as nitriding and chrome plating, can improve die wear resistance and lifespan,ensuring a smooth extrusion process.
- Selecting materials like H13, which offer excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance, ensures long-termstable die operation.

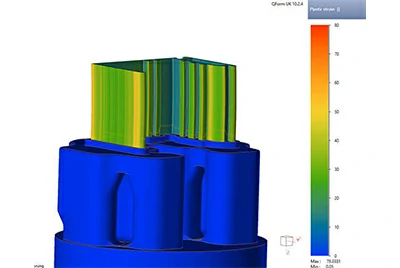
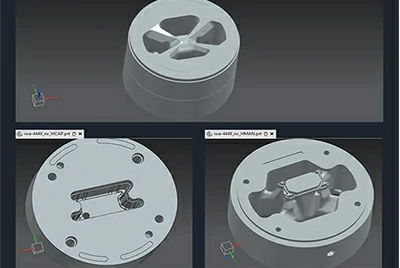

At Chalco, we manufacture our own dies and also purchase dies from independent die manufacturers.
We develop design support tools to achieve efficient extrusion die design, correct dies to optimize productionefficiency, and study die performance.
We continuously improve our manufacturing processes to reduce your costs by using the following methods:
- Material flow simulation in dies
- Integration with computer-aided design systems to calculate flow resistance at ports, mandrel deflection, andstress in the web
- Heat treatment of tool steels
- Surface treatment of dies using methods such as nitriding, nitriding and carburizing, chemical vapor deposition,and plasma vapor deposition.

Aluminium extrusion die cost
The complexity of the die is a key factor in determining the cost of aluminium extrusions. There are also certainlimitations to reducing unit prices by increasing quantity.
The cost of aluminium extrusion dies is influenced by several factors, and the following points should beconsidered:
- Efficient die design and process planning are crucial to reducing overall costs.
- Advanced design tools, such as feature-based neural networks and CAD systems, help optimize the design process,reducing errors and rework.
- Regular die maintenance and repairs help extend the die's lifespan and reduce downtime and failure-relatedcosts.
- Material selection should balance initial production costs, performance, and die lifespan.
- High-quality tool steels like H13, although more expensive initially, save on downtime and maintenance costs inthe long run due to their excellent wear resistance and durability.
- Profile complexity increases die costs, manufacturing process complexity, and maintenance expenses.
- High production volumes can make investing in more expensive die materials or processes more cost-effective,thus lowering the per-unit cost.
To balance cost and performance, manufacturers typically adopt cost-saving strategies, such as:
- Using standardized die profiles whenever possible
- Optimizing die design to improve material flow and reduce wear
- Implementing preventive maintenance and rework plans to extend die life.

Aluminium extrusion die manufacturers
- Chalco: Primarily offers aluminium products and extrusion die manufacturing, along with aluminium processingequipment.
- Hydro Extrusion North America: Provides aluminium extrusion dies and forming services, with multiplemanufacturing facilities.
- Alcoa Corporation: A global leader in aluminium production, also offering aluminium extrusion die solutions.
- Exlabesa Aluminium: Provides aluminium extrusion dies and profiles, widely used in various industries, includingconstruction and automotive.
- Franz A. Wagner GmbH: Specializes in custom aluminium extrusion dies, widely used across different industries.
- SMS Group: Offers aluminium extrusion dies and complete aluminium processing solutions, one of the world'sleading equipment suppliers.
Choose Chalco for our industry-leading technology and one-stop services to effortlessly meet your aluminiumextrusion needs. Click here to contact us for professional support!
Instant Quote
Industry standards and best practices
Adhering to industry standards and best practices is crucial for ensuring product quality, safety, and regulatorycompliance.
Some of the prominent organizations and associations responsible for establishing these guidelines for the aluminiumextrusion industry include:




The extrusion process typically involves the following steps
- Billet preheating: The aluminium billet (solid cylindrical log) is preheated to the required temperature,usually around 700-930°F (370-500°C), depending on the alloy, to achieve the necessary plasticity for extrusion.
- Container loading: The preheated billet is loaded into a heated container, which is part of the extrusion press.
- Stamping advancement: A hydraulic stamping press applies immense pressure, usually between 1,000 to 15,000 tons,forcing the softened aluminium through the die opening.
- Profile extrusion: As the aluminium is pushed through the die, it takes the shape of the die opening, formingthe desired profile.
- Profile cooling and treatment: The extruded profile is cooled either by air or water, then transferred forfurther processing, such as stretching, machining, and surface treatment.
Throughout the extrusion process, the die plays a crucial role in maintaining dimensional accuracy, surface finish,and overall product quality.
Factors such as die design, material flow, and thermal management significantly affect extrusion quality andefficiency.
How long do extrusion dies last?
Profile design (such as thin walls, unbalanced shapes, and protruding legs) can lead to heat buildup and unevenpressure, which are the biggest factors shortening die lifespan.
Experienced extrusion machine designers create appropriate dies to control heat and pressure imbalances and reduceextrusion speed to extend die life, but ultimately, dies must be replaced. Fortunately, most extrusion machines canbear the cost of die replacement.
However, designers should understand which design decisions will have the most significant impact on upfront diecosts before sending designs to the aluminium extrusion machine.
Adjusting profile design, tolerance settings, and alloy materials can save thousands of dollars in die costs.
Maintenance and troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of aluminium extrusion dies are crucial for ensuring stable performance,maximizing die lifespan, and minimizing downtime.
Some common die issues and maintenance practices include:
- Over time, die openings wear due to high pressure and temperature. Regular inspection and maintenance can extenddie life.
- Scratches and buildup on the die surface can affect profile quality. Proper cleaning and surface treatment canmitigate these issues.
- Uneven heating or cooling can cause deformation or uneven material flow. A good thermal management system isessential.
- Misalignment or inadequate support of die components can affect dimensional accuracy and shorten die life,requiring regular alignment adjustments.
- A comprehensive preventive maintenance plan, including regular inspections and cleaning, can significantlyextend die life and reduce downtime.
- Advanced diagnostic tools (such as Finite Element Analysis) help identify root causes and provide effectivesolutions.




Collaboration and communication
Successful aluminium extrusion projects typically require the combined efforts of various stakeholders, includingdie designers, manufacturers, extruders, and end-users.
Effective communication and coordination are crucial for achieving the desired outcomes.
Designers: Die designers are crucial in turning product requirements into optimized die designs that meetperformance, quality, and cost goals. Close collaboration with manufacturers and extruders ensures compatibilitywith existing processes.
Manufacturers: Die manufacturers bring expertise in die fabrication, material selection, and production processes.They ensure the design is manufacturable within tolerances and quality standards.
Extruders: Extruders have deep knowledge of extrusion processes, including press capabilities, die needs, andprocess parameters. Their input ensures the die meets extrusion conditions and production requirements.
End-users: End-users provide key insights into functional, performance, and application requirements, which shouldbe incorporated into the design and process.
Open communication and regular information exchange among stakeholders help identify and address potential issuesearly in the project.
This collaboration ensures successful die design and manufacturing while driving continuous improvement andinnovation in the aluminium extrusion industry.

Emerging trends and future developments
The aluminium extrusion industry is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements, changes in marketdemand, and the push to improve efficiency, precision, and die lifespan.
Some emerging trends and future developments shaping the aluminium extrusion technology landscape include:
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to optimize die design and processes, improvingefficiency, reducing waste, predicting the best extrusion parameters, and enabling predictive maintenance.
- While new coatings are continuously being developed, in our experience, their feasibility and cost-effectivenessstill need further validation in most applications.
- Additive manufacturing technologies, such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM), are being used to create complex diegeometries, improving thermal management and increasing production efficiency.
- Advanced simulation software and modeling technologies are widely applied in die design to help predict materialflow, thermal behavior, and optimize design iterations, enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- The aluminium extrusion industry is driving sustainable energy-saving practices by optimizing designs, exploringalternative materials and manufacturing processes, and implementing recycling and reuse strategies.
These advancements are pushing the aluminium extrusion industry towards higher precision, efficiency, andsustainability, meeting the evolving demands of sectors like automotive, aerospace, and construction.