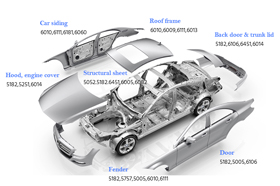
Both 6061 and 6082 are heat-treatable aluminum alloys from the 6000 series, offering good strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and outstanding machinability. They are widely used in structural engineering, machinery manufacturing, transportation, marine, and construction industries.

Compared to 6061 aluminum, 6082 has higher mechanical strength, especially in the T6 temper, making it ideal for structural components that require greater load-bearing capacity. However, 6082 has slightly lower weldability than 6061, and in complex structures or thin-wall welding applications, additional process control may be required to prevent hot cracking.
Instant QuoteProduct differences
6061 aluminum products

6061 Aluminum Tube

6061 Aluminum Round Bar

6061 Aluminum Sheet Plate

6061 Aluminum Automotive Profile

6061 Aerospace Aluminum Wire

6061 Aluminum Block

6061 Aluminum Flat Bar

6061 Aluminum Angle

6061 Aluminum Tubular Buspipe
6082 aluminum product

6082 Aluminum Sheet Plate

6082 Aluminum Round Bar

6082 Aluminium Tube

6082 Aerospace Aluminum Plate

6082 Aerospace Aluminum Extrusions

6082 Aerospace Forgings
Different tempers
| Alloy | Common Tempers |
| 6061 aluminum | T6, T651, T4, O, T42, T62, T6511 |
| 6082 aluminum | T6, T651, T4, O |
6061-T6 is one of the most commonly used heat-treated tempers of 6061 aluminum alloy. It is obtained through solution heat treatment followed by artificial aging. This temper offers a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability, making it widely used in structural components and the aerospace industry.
6061-T651 is a stress-relieved version of T6. After heat treatment, the material is stretched to reduce residual internal stresses, improving dimensional stability. It is ideal for high-precision machining applications.
6082-T6 is the standard high-strength temper of 6082 aluminum alloy, produced by solution treatment and artificial aging. With higher strength than 6061-T6, it is widely used in structural engineering such as bridges, cranes, and transportation equipment.
6082-T651 is the stress-relieved version of 6082-T6, offering better stability and reduced risk of deformation during machining. It is especially suitable for large or high-precision components.
Different chemical compositions
| Element | 6061 | 6082 |
| Aluminium (Al) | 95.85 – 98.56% | 95.2 – 98.3% |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.80 – 1.20% | 0.60 – 1.20% |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.40 – 0.80% | 0.70 – 1.30% |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤ 0.70% | ≤ 0.50% |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.15 – 0.40% | ≤ 0.10% |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.04 – 0.35% | ≤ 0.25% |
| Zinc (Zn) | ≤ 0.25% | ≤ 0.20% |
| Titanium (Ti) | ≤ 0.15% | ≤ 0.10% |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 0.15% | 0.40 – 1.00% |
| Others (Total) | ≤ 0.15% (≤ 0.05 each) | ≤ 0.15% (≤ 0.05 each) |
6061 vs 6082 aluminum properties
Tensile strength
Tensile strength represents the maximum tensile stress a material can withstand before breaking.
6061 aluminum: Ultimate tensile strength is approximately 340 MPa, suitable for medium-strength structural components.
6082 aluminum: Around 410 MPa, offering higher strength for heavy-load applications.
Yield strength
Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform permanently.
6061 aluminum: Approximately 320 MPa, providing a good balance of strength and ductility, ideal for general structural use.
6082 aluminum: About 370 MPa, capable of withstanding higher stresses before deformation, suited for heavy-duty scenarios.
Shear strength
Shear strength is the material's ability to resist shear forces internally.
6061 aluminum: Shear strength ranges from 84–210 MPa, adequate for most moderate shear load applications.
6082 aluminum: Slightly higher shear strength, around 84–220 MPa, better for structures under greater shear force.
Elastic modulus
Indicates material stiffness during elastic deformation.
6061 and 6082: Both have an elastic modulus of approximately 69 GPa, offering similar stiffness and elastic behavior.
Fatigue strength
Fatigue strength is the stress limit below which a material can endure cyclic loading without fracturing.
6061 aluminum: Fatigue strength is about 58–110 MPa, suitable for moderate cyclic stress applications.
6082 aluminum: Slightly higher, at 55–130 MPa, better for frequently loaded structures.
Elongation at break
Measures ductility as the percentage of elongation before fracture.
6061 aluminum: Ranges from 3.4% to 20%, allowing easy forming of complex shapes.
6082 aluminum: Around 6.3% to 18%, with slightly lower ductility but still good formability.
Overall mechanical performance
In summary, 6082 aluminum generally surpasses 6061 aluminum in tensile strength, yield strength, shear strength, and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for high-stress and heavy-load applications. On the other hand, 6061 aluminum offers better ductility and machinability, making it widely used where ease of processing and forming is critical. Both alloys share similar stiffness and density, making them suitable for lightweight structural applications.
Differences in applications
Applications of 6061 aluminum alloy
- Aerospace components (e.g., connectors, structural brackets)
- Bicycle frames, motorcycle parts
- Marine structures, deck railings
- Industrial equipment frames and mechanical parts
- Mold base plates, CNC machined parts
- Automation equipment supports, rail components
- Furniture profiles, display racks, door and window systems
Advantage:
6061 offers excellent weldability and is well-suited for complex structural designs and machining needs, making it ideal for versatile engineering applications.
Applications of 6082 aluminum alloy
- Bridge structures, lifting frames
- Cranes, aerial work platforms, construction machinery arms
- Rail vehicle frames, subway screen doors
- High-pressure fluid pipelines, oil transportation systems
- Construction scaffolding, solar panel mounting systems
- Port machinery, container frames
- Offshore platform components


Advantage:
With higher strength, 6082 is better suited for load-bearing and high-stress structures, and is widely used in European construction and transportation engineering projects.
Corrosion resistance differences
6061 aluminum alloy offers good corrosion resistance, especially after welding, maintaining stable protective properties. It performs well in various typical environments such as marine structures, piping systems, and outdoor frameworks. It is particularly effective under general industrial and coastal atmospheric conditions.
6082 aluminum alloy demonstrates better resistance to stress corrosion, thanks to its higher manganese content. It is especially suitable for long-term load-bearing applications in high-moisture, high-salt environments such as bridges, railways, and heavy-duty structural components.
Electrical conductivity differences
Both 6061 and 6082 aluminum alloys have relatively good electrical conductivity compared to other structural metals, but there are slight differences due to their chemical composition.
- 6061 aluminum has an electrical conductivity of approximately 40–43% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard).
- 6082 aluminum has a slightly lower conductivity, typically around 37–41% IACS.
The presence of alloying elements like manganese in 6082 slightly reduces its conductivity compared to 6061. As a result, 6061 is generally more suitable for applications where higher conductivity is desired, such as in certain electrical or thermal conduction components, while 6082 is preferred in structural applications where strength is more critical than conductivity.
Weldability differences
6061 aluminum alloy offers excellent weldability and is one of the most welding-friendly materials in the 6000 series. Its heat-affected zone remains structurally stable during welding, with minimal loss of weld strength. It is compatible with various welding methods such as TIG and MIG, making it widely used in welded structures like frames, marine components, and automotive parts.
In comparison, 6082 aluminum alloy is also weldable but has a slightly higher sensitivity to hot cracking due to its higher silicon and manganese content. Its mechanical properties tend to degrade more noticeably after welding. Therefore, 6082 is better suited for applications with limited welding or those where post-weld heat treatment can be applied to restore strength.
Comparison of machinability
6061 aluminum is highly regarded for its excellent machinability. It can be easily cut, drilled, and formed using standard machinery and general-purpose lubricants. Its characteristics allow for high-speed machining, tight tolerances, and fine surface finishes, making it a popular choice across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and general engineering.
6082 aluminum, while still machinable, poses greater challenges due to its higher strength and hardness. Machining 6082 requires specialized lubricants and equipment to handle its increased hardness, which leads to higher tool wear and necessitates reduced cutting speeds. In contrast, 6061 can typically be processed with standard machines and lubricants, reducing costs and increasing manufacturing flexibility.
When machining 6082 aluminum, high-quality cutting tools made from materials like carbide are recommended, along with appropriate cooling and lubrication techniques to manage the heat generated during processing. The choice of lubricant is critical for both 6061 and 6082. For 6061, general-purpose lubricants usually provide sufficient cooling and lubrication to ensure smooth machining and a good surface finish. In comparison, machining 6082 requires advanced lubricants with superior cooling and lubricating properties to handle the higher heat levels effectively.
In summary, 6061 aluminum is easier to machine with standard tools and lubricants, making it well-suited for fast, complex operations. Although 6082 is more difficult to machine due to its strength and hardness, it can still be processed efficiently with the right tools and techniques.
Price differences
When comparing the cost of 6061 aluminum and 6082 aluminum, several key factors should be considered. Generally, 6082 aluminum is more expensive than 6061 due to the addition of alloying elements like manganese, which enhance its strength and durability. 6061 aluminum is widely recognized for its cost-effectiveness and broad availability, whereas the higher price of 6082 reflects its superior mechanical properties.
6061 is more commonly available—especially in North America—making it a popular choice across various industries. Its wide availability also helps keep its price relatively low. In contrast, 6082 is more prevalent in the European market, and limited availability in other regions can contribute to higher costs.
The machining and welding costs for these alloys also differ. 6061 aluminum is easier and cheaper to process, requiring only standard machinery and general-purpose lubricants. On the other hand, 6082 may require specialized tools and lubricants, increasing production expenses. While both alloys have good weldability, 6082 may demand more advanced techniques, which can raise welding costs.
Although 6082 aluminum has a higher initial cost, its excellent strength and corrosion resistance can reduce maintenance needs and extend service life—making it a more cost-effective choice for high-performance applications. When deciding between the two, it's important to consider your specific industry requirements and application needs.
Ultimately, the choice between 6061 and 6082 aluminum should be based on the unique demands of your project.
What Services Can Chalco Provide?
If you are considering purchasing 6061 or 6082 aluminum alloy products, Chalco offers a range of professional services to help you complete your project efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively.
Free samples
Chalco offers free samples for your project testing. Place your order only after confirming the material performance—giving you peace of mind. Contact us.
Discount pricing
Returning customers and bulk purchasers are eligible for special discounts, helping you stay competitive in price.
In-stock supply of multiple specifications
We provide 6061 and 6082 aluminum plates, bars, tubes, and profiles in commonly used tempers such as T6, T651, and T4, ensuring fast delivery for urgent orders.
High-precision custom machining
We offer cutting, milling, tapping, drilling, and CNC machining services, with saw cutting tolerances up to ±0.005 inch, meeting the needs of high-precision components.
Material certification and quality reports
All products come with a Mill Test Certificate (MTC), chemical composition analysis, and mechanical property reports, fully compliant with international standards such as ASTM, EN, and GB.
Custom packaging and export services
We provide tailored moisture-proof and impact-resistant packaging, and support sea freight, air freight, LCL, and FCL export. Complete export documentation is available, including Certificate of Origin (CO), packing list, and commercial invoice.
Tailored solutions
Chalco offers one-stop solutions including material selection advice, temper customization, machining support, and export logistics. Whether your priority is strength, machinability, or weldability, we will recommend the most suitable 6061 or 6082 aluminum alloy based on your project requirements.