For many engine and brake engineers, conventional aluminum alloys are already at their limit.
Pistons crack at the crown, ring grooves wear out early, cast iron brake discs add too much weight, and it becomes difficult to control thermal fatigue and NVH at 250–350 °C.
Chalco's low-CTE, high-temperature CeramAl ceramic aluminum matrix composites are developed to solve exactly these problems. They boost strength at 300 °C, extend piston life, cut component weight by up to 50–60% versus steel or cast iron, and typically save around 2–5% fuel while improving damping and dimensional stability under cyclic thermal loads.
Chalco provides customized high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composite solutions
For conditions involving continuous heating and frequent thermal cycling, Chalco introduces in-situ nano-ceramic particles into various aluminum alloy matrices (aluminum as the base, nano-ceramics as the reinforcement).
By precisely controlling the volume fraction, particle size/morphology, and spatial distribution, the material maintains its strength and stiffness even at medium to high temperatures.
It also achieves low thermal expansion (CTE tailored to target values), excellent thermal conductivity, and dimensional stability, along with strong high-temperature fatigue and creep resistance.
- Matrix options: Supports 2xxx / 6xxx / 7xxx alloy systems, optimized for the right balance of strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and machinability based on application needs.
- Particle control: Adjustable volume fraction, particle size, shape, and distribution—customized for low-CTE thermal matching, high-temperature wear resistance, creep resistance, and long thermal cycle life.
- Process flexibility: Full-process support including extrusion, rolling, forging, ring rolling, machining, electroless nickel plating, vacuum brazing, and welding, with process window recommendations.
Chalco establishes strict quality control on flatness, roughness, and coating adhesion, ensuring batch consistency and full traceability.
Popular high-temperature ceramic aluminum alloys
With outstanding mechanical performance at elevated temperatures, our high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites have earned strong market recognition, far outperforming conventional aluminum alloys.
Our current key products include heat-resistant high-stiffness alloy (JG109X) and heat-resistant high-strength alloy (JG201).
Heat-resistant high-stiffness (JG109X) ceramic aluminum matrix composite
Exhibits excellent high-temperature wear resistance and fatigue strength, ideal for engine pistons and other components requiring superior heat and wear resistance.
Contact us now
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HB, room temperature) | |
| 300℃ | 350℃ | ||
| Conventional aluminum alloy (piston) | 120-130 | 80-85 | 90-120 |
| JG109X ceramic aluminum matrix composite (piston) | 150-170 | 90-110 | 120-140 |
| Improvement | +25–30 % | +13–29 % | +17%-33% |
JG109X ceramic aluminum matrix composite applications:
Used in engine pistons, the JG109X composite maintains high stiffness and wear resistance under high temperature and repeated thermal cycling, significantly extending service life and enabling lightweight design.
-
 Fuel-saving pistons
Fuel-saving pistons
FT diesel piston: fuel consumption reduced by 4.7%
KMS diesel piston: fuel consumption reduced by 2.7%
-
 Low-emission pistons
Low-emission pistons
FT diesel piston: upgraded from Euro IV to Euro V
THC reduced from 0.145 to 0.121 (↓16.6%), CO reduced from 8.920 to 3.686 (↓58.7%), NOx reduced from 0.084 to 0.036 (↓57.1%)
-
 High-power pistons
High-power pistons
HC diesel piston: a 132 mm bore engine can achieve the efficiency of a 150 mm engine.
HC diesel piston: a 107 mm bore engine can achieve the efficiency of a 132 mm engine.
-
 Long-life pistons
Long-life pistons
HC diesel piston: replacement interval extended from 50 hours to 80 hours, increasing lifespan by 60%.
DML diesel piston: full-power, full-load operation time increased from 700 hours to 1170 hours.
HM diesel piston: ring groove failure time extended from 50 hours to 110 hours, improving lifespan by 120%.
-
 Lightweight and cost-efficient
pistons
Lightweight and cost-efficient
pistons
DZ gasoline piston: eliminates ring inserts with an integrated design, reducing weight by 13.5% and cost by 9%.
YC diesel piston: replaces all-steel pistons, achieving 50% weight reduction and 50% cost savings.
HC diesel piston: replaces all-steel pistons, achieving 50% weight reduction and 50% cost savings.
-
 Connecting rods
Connecting rods
Made with high-temperature nano-ceramic aluminum alloy, the connecting rods achieve significant weight reduction.
The associated suspension system reaches a 1:2 weight reduction ratio — for every 10% weight reduction, fuel savings of 1.5–2.5% can be achieved.
Heat-resistant high-strength (JG201) ceramic aluminum matrix composite
The JG201 ceramic aluminum matrix composite offers exceptional high-temperature strength and thermal stability.
It is designed for components requiring superior heat resistance and load-bearing capacity, such as engine cylinder liners and cylinder heads.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | |
| 25℃ | 300℃ | |
| High-strength heat-resistant aluminum alloy | 480 | 155 |
| JG201 ceramic aluminum matrix composite | 550 | 230 |
| Improvement | +15% | +48% |
JG201 ceramic aluminum matrix composite applications:
Used in engine blocks and cylinder heads, JG201 delivers about 35% higher wear resistance at room temperature compared to conventional aluminum alloys, while reducing block weight by approximately 17% without compromising strength.
Contact us now
High-temperature (HD021) ceramic aluminum matrix composite
HD021 is a gravity-cast T5-state high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composite, reinforced with nano-ceramic particles.
It maintains strength, dimensional stability, good thermal conductivity, and improved ductility in the medium-to-high temperature range, making it ideal for long-term thermal cycling and high-temperature load conditions.
| Material (Temperature) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
| HD021 (25 °C) | 225–255 | 210–235 | 1.0 |
| HD021 (150 °C) | 220–250 | 200–225 | 1.5 |
| HD021 (250 °C) | 185–210 | 160–180 | 2% (250°C) |
| HD021 (300 °C) | 140–160 | 120–135 | 2.5% (300°C) |
| HD021 (350 °C) | 95–110 | 75–85 | 3% (350°C) |
Typical properties:
- Elastic modulus (GPa): 75–80
- Density (g/cm³): 2.81
In addition, Chalco provides other high-temperature aluminum alloy solutions such as 2618, 2219, 2014, 2024, and 4032, with rapid material selection based on your target temperature range, strength, and CTE requirements.
-
2618 / 2618A Aluminum
Commonly used for forged pistons, connecting rods, and turbine components.
Retains excellent hot strength and fatigue resistance at 200–250 °C.
Ideal for high-temperature cyclic loads.
-
2219 Aluminum
A widely used grade for aerospace tanks and welded structures.
Offers good weldability and strength retention at 150–200 °C.
Outperforms conventional 6xxx and 7xxx alloys.
-
2014 / 2024 Aluminum
General-purpose high-strength forging alloys.
Maintain superior performance over 6xxx and 7xxx alloys at 125–150 °C.
Suitable for medium-temperature load-bearing structures.
-
2139 / 2050 / 2198 Aluminum
Balanced medium-temperature strength and damage tolerance.
Ideal for aerospace lightweight structures.
Designed for operating at 120–160 °C.
-
4032 Aluminum
Commonly used in forged pistons.
Features low thermal expansion and excellent wear resistance.
Stable thermal performance at 150–200 °C.
-
8009 Aluminum
Produced via rapid solidification or powder metallurgy.
Maintains high strength even at 250–300 °C.
Suitable for high-temperature lightweight structural components.
| Alloy | Main form | Typical working temp. | Best for |
| JG109X | Cast pistons, forgings | up to ~350 °C | High-stiffness, high wear resistance pistons |
| JG201 | Blocks, cylinder heads | up to ~300 °C | High-strength load-bearing engine components |
| HD021 | Gravity cast components | 150–350 °C | Long-term thermal cycling & high-temperature load parts |
Not sure which alloy fits? Tell us your target temperature, load, and CTE window, and we will propose the best alloy and process route.
Advantages of high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites
- Retain the lightweight characteristics of aluminum alloys, significantly reducing component and overall system mass.
- Achieve ultimate tensile strength over 800 MPa; higher specific strength than titanium alloys — lighter yet stronger.
- Elastic modulus up to ≈95 GPa; higher specific stiffness than titanium, offering superior deformation resistance.
- Rotating bending fatigue improved by ~94% over 7xxx alloys and ~87% over 2xxx alloys; axial double-hole fatigue about 30% higher than Alcoa 2060 aluminum-lithium alloy.
- Higher hardness and lower wear loss, ensuring precise tolerance control and long-term dimensional stability.
- Maintain the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys, compatible with coating and plating systems.
- Significantly enhanced high-temperature strength and creep resistance, delivering superior thermal fatigue durability.
- Compatible with multiple processing routes: extrusion, rolling, forging, drawing, ring rolling, superplastic forming, machining, welding, and 3D printing.
Performance of high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites
Key performance highlights vs. conventional high-temperature aluminum alloys:
- High-temperature tensile strength: up to +48% at 300 °C (JG201 vs. ZL205A).
- Creep resistance: creep stress index at 350 °C increased from 4.2 to 12.
- Fatigue strength: +7–15% higher at 120–400 °C over Mahle 174 alloy.
- Piston life: ring groove life up to ×2.2; overall piston life +60% or more.
- Fuel saving: 2–5% in heavy-duty truck and passenger engine applications.
- Damping: 2× cast iron, 5× magnesium alloys, 10× conventional aluminum alloys.
High-temperature strength performance
Under high-temperature conditions, ceramic aluminum matrix composites maintain excellent strength, with a significantly higher creep stress index, ensuring greater durability and reliability.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Creep Stress Index | |
| 300°C | 350°C | 350 °C, 40 MPa | |
| Mahle 174 alloy (Germany) | 120-140 | 85-100 | 4.2 |
| High-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composite | 140-160 | 95-110 | 12 |
Tested by: Binzhou Bohai Piston Co., Ltd., Shandong, China
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | |
| 25 °C | 300 °C | |
| High-strength heat-resistant aluminum alloy (ZL205A) | 480 | 155 |
| High-temperature high-strength ceramic aluminum matrix composite | 550 | 230 |
Tested by: China North Industries Group Corporation, No.59 Research Institute
High-temperature fatigue performance
The thermal fatigue resistance of ceramic aluminum matrix composites is significantly enhanced.
Even under repeated thermal cycling and high-temperature loads, they maintain a longer service life and higher reliability.
| Fatigue (50×10⁶ cycles) LW / MPa | Mahle 174 alloy (Germany) | High-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composite | Improvement (%) |
| 120°C | 105 | 113 | +7.62% |
| 150°C | 85 | 92 | +8.24% |
| 200°C | 70 | 78 | +11.43% |
| 250°C | 50 | 55 | +10.00% |
| 350°C | 40 | 46 | +15.00% |
| 400°C | 35 | 39 | +11.43% |
Tested by: Binzhou Bohai Piston Co., Ltd., Shandong, China
Damping performance
The damping performance of ceramic aluminum matrix composites is about 2× that of cast iron, 5× that of magnesium alloys, and 10× that of conventional aluminum alloys.
They effectively suppress vibration and noise, improving overall NVH (Noise, Vibration, and Harshness) performance.
| Material | A356 | 10% TiB2 /A356 |
| Damping Absorption Factor Q⁻¹ (×10⁻³) | 1.2-2.4 | 18-23 |
High-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites offer high damping and low thermal expansion, with optional neutron absorption and shielding capabilities, making them ideal for thermal stability and vibration control applications.
Material Coefficient of Thermal Expansion CTE (×10⁻⁶ K⁻¹, at room temperature A356 21-23 10%TiB2/A356 15-18 (reduced by one-third)
Thermal neutron shielding performance
| Material | Absorption Coefficient μ (cm²/g) |
| Aluminum alloy | 10⁻² |
| Steel | 10⁻¹ |
| Ceramic aluminum (Al–TiB₂) | 10¹ – 10² |
Cold neutron shielding performance (neutron wavelength 0.9 mm)
| Material | Cold Neutron Transmittance |
| Steel plate (1 mm thick) | 85–95% |
| Aluminum plate (1 mm thick) | >95% |
| 1% TiB/Al (1 mm thick) | 55% (LLB) |
| 15% TiB/Al (1 cm thick) | Full shielding (LLB) |
Real-world applications of high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites
To meet China National V, VI, and higher emission standards, engines require increased power density and longer piston life. Traditional high-temperature aluminum alloys can no longer balance strength, wear resistance, thermal fatigue, and corrosion resistance.
Our high-temperature nano-ceramic aluminum matrix composites (CeramAl) deliver remarkable improvements in high-temperature tensile strength, thermal fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance compared with conventional high-temperature aluminum alloys, and have been successfully applied to various engine internal components.Engine – piston application cases
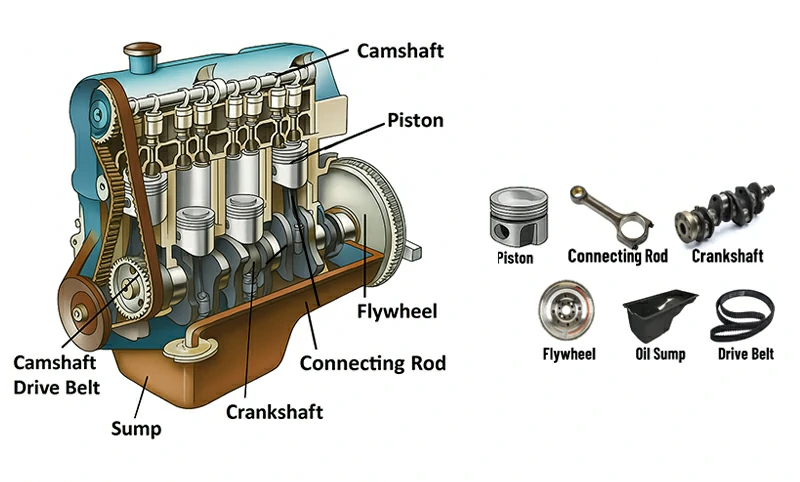
- Under 23 MPa explosion pressure and 88 kW/L power density, pistons maintain stability at high speed and high torque, with a significantly extended lifespan under high explosion pressure.
- Replaced forged steel pistons (China VI project): weight reduced by ≈58%, system cost reduced by ≈43%, and friction loss decreased by over 4%.
- Methanol engine pistons: skirt area reduced by about 25%, lowering friction and noise; methanol fuel consumption decreased from 510 to 467 g/kWh (≈8.4% reduction).
- Heavy-duty truck pistons: fuel savings of 2.0–3.2%, smoke opacity reduced by 43.9%, and PM emissions reduced by 31%.
In engine platforms, the cylinder block, cylinder head, and flywheel housing also benefit from high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composite solutions.
-
Cylinder block / cylinder head

Enhanced wear resistance, strength, and lifespan, with overall engine weight reduction. Maintains dimensional stability and reliable sealing under long-term thermal cycling.
-
Flywheel housing

Approximately 60% lighter than cast iron, suitable for long-life and high-frequency vibration conditions, significantly extending service life.
Brake disc application cases
CeramAl (SiC particle–reinforced aluminum matrix composite) is used in urban rail, passenger cars, and high-speed train brake discs, showing outstanding performance in thermal fatigue life, wear resistance, and high-temperature friction stability.
It also offers significant weight reduction, easy machinability, and recyclability, perfectly meeting the needs of lightweight and high-reliability vehicles.
- Resistant to thermal cracking under repeated braking and air-cooling cycles.
- Stable friction coefficient with minimal fade, ensuring consistent braking feel.
- Significantly lighter than cast iron or cast steel, improving acceleration, efficiency, and reducing unsprung mass.
- Reinforced with high-hardness, high-modulus particles, reducing wear and deformation.
- Machining-friendly and fully recyclable, offering lower lifecycle cost for the entire vehicle.
Our partners in high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites
We collaborate closely with many industry-leading organizations and brands, focusing on the research, development, and application of high-performance ceramic aluminum matrix composites.
- CRRC (China Railway Rolling Stock Corporation): the world's leading manufacturer of rail transit equipment.
- AVIC (Aviation Industry Corporation of China): a major force in China's aviation industry, co-developing aerospace materials and components.
- CASIC (China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation): applying high-performance ceramic aluminum composites in aerospace systems.
- NORINCO (China North Industries Group): utilizing ceramic aluminum matrix composites in weaponry and defense programs.
- CNGC (China South Industries Group): supporting lightweight and durable weapon system development with ceramic aluminum composite technology.
- COMAC (Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China): applying ceramic aluminum composites in major projects such as the C919 aircraft.
- AECC (Aero Engine Corporation of China): a leader in aero engine R&D and manufacturing, widely applying ceramic aluminum matrix composites in aero engines and key structural components.

Our R&D and production equipment
Our company is equipped with advanced research and manufacturing facilities, ensuring the high quality and efficient production of ceramic aluminum matrix composites and related products.
Ceramic aluminum matrix composite production lines
We operate in-situ synthesis, special casting, semi-continuous casting, and additive manufacturing powder production lines, ensuring precise production of various CeramAl alloy grades.
Large-scale production equipment
Over 100 sets of high-end equipment, including reaction synthesis furnaces, counter-gravity casting systems, and large-format SLM metal 3D printers, support large-scale and precision manufacturing.
Analytical and testing instruments
More than 20 high-precision testing systems, such as photoelectric direct-reading spectrometers and image analyzers, are used to strictly control product quality and ensure batch stability and reliability.
High production capacity
With an annual output of 18,000 tons of ceramic aluminum matrix composites and components, we can meet the needs of large-scale customized production.
Inspection and laboratory equipment
Our facilities include real-time X-ray imaging systems, fatigue testing machines, tensile testers, hydrogen analyzers, oxygen-nitrogen-hydrogen determinators, microscopes, X-ray diffractometers, particle size analyzers, and inductively coupled emission spectrometers, ensuring all products meet the highest industry standards.


Supply forms & delivery
- Forms: gravity cast blocks, forged blanks, rings, discs, machined pistons and brake discs.
- Typical sizes: piston blanks up to ØXXX mm, brake discs up to ØXXX mm (customizable).
- MOQ: prototype batches from XX pcs; mass production from XX pcs (depending on part type).
- Lead time: sample 4–6 weeks, regular production 8–10 weeks after order and drawing confirmation.
Packaging and transportation of high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites
To ensure the appearance and performance stability of ceramic aluminum matrix composites during global transportation, we use multi-layer protection and offer customized packaging options.
- Inner protection: Functional surfaces are covered with PE protective film, with dust-free interleaving sheets between plates; coated or mirror-finish parts are individually wrapped for scratch and pressure protection.
- Moisture and corrosion protection: VCI anti-rust film combined with vacuum-sealed aluminum-plastic barrier bags, containing desiccants and humidity indicator cards (HIC); extra protection available for marine shipments.
- Structural reinforcement: EVA cushioning, custom positioning pallets, and external corner guards, wrapped with stretch film and strapping; all packages include shock and tilt warning labels.
- Wooden crates and certification: Plywood cases compliant with ISPM 15, four-way forklift entry; recommended single-crate weight ≤ 1200 kg (typically 300–800 kg).
- Accompanying documents: Packing list, invoice/bill of lading, EN 10204 3.1 material certificate, and inspection reports (dimensions, flatness, coating, etc.) provided upon request.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
What is an aluminum matrix composite (Al-MMC / AMC)?
An aluminum matrix composite is a material composed of aluminum or aluminum alloy as the matrix, reinforced with phases such as particles, whiskers, short fibers, or nanoparticles (e.g., SiC, Al₂O₃, TiC, TiB₂, B₄C, carbon fibers, etc.).It is lightweight (low density), designable (strength, stiffness, CTE, and thermal conductivity can be tailored as needed), wear-resistant, fatigue-resistant, and dimensionally stable.
Manufacturing methods include in-situ reaction, powder metallurgy, stir/low-pressure/extrusion casting, pressure infiltration, spray deposition, and additive manufacturing (3D printing).
How strong are aluminum matrix composites?
Typical tensile strength ranges from 300–600+ MPa, and can reach 600–700+ MPa with high reinforcement and optimized heat treatment.
The elastic modulus can increase from the usual 70 GPa (for aluminum alloys) to 80–120 GPa.
They show major improvements in fatigue and wear resistance, though elongation may decrease as reinforcement content increases.
Get samples and quick quotation
Customize materials based on your target CTE, temperature range, and thermal conductivity — submit your drawings and operating conditions, and we'll provide a material proposal, process window, quotation, and lead time within 48 hours.