Chalco's ceramic aluminum matrix composites use in-situ nano-ceramics to achieve high strength and stiffness, low CTE, and thermal stability. They keep low density while balancing wear resistance and service life.
We provide full-process customization for wrought (plate/profile/forging), casting, and LPBF powder. This enables integrated complex structures and rapid delivery, already applied in the C919 airframe, engine pistons, and steering knuckles.
Why choose Chalco ceramic aluminum matrix composites (Al-MMC)
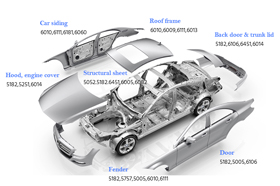
Use lighter materials to build stronger, more stable, and more cost-efficient parts. This is the direct value we create for engineering teams.
Cast instead of forge to cut cost and lead time
Near/net-shape forming slashes forging and heavy machining. It shortens lead time, lowers total cost, and makes integrated complex structures easier to deliver.
Stronger and more stable performance
At the same mass, you get higher strength/stiffness/fatigue life. Dimensions stay stable under thermal cycling with better vibration damping, boosting assembly consistency and service life.
Precise customization to target parameters
Tune the volume fraction, particle size, morphology, and spatial distribution of in-situ nano-ceramics.
Match with 2xxx/6xxx/7xxx matrices. Design backward to CTE/working temperature range/thermal conductivity/stiffness for "material-structure-process" co-optimization.
Process-friendly and ready for volume production
Compatible with low-pressure casting (T6), squeeze casting (T6), and die casting (partial no-heat-treat).
Also covers wrought routes (extrusion, rolling, forging, drawing, ring rolling, superplastic forming), machining, welding, and LPBF 3D printing, with controllable yield and batch consistency.
Chalco ceramic aluminum matrix composites products
Chalco's ceramic aluminum matrix composites cover four systems: high-strength wrought, high-temperature, casting, and additive powders.
They target the strict demands of aerospace and automotive for strength/stiffness, thermal fatigue and dimensional stability, lightweighting, and cost, and are validated in the C919 airframe, engine pistons, and steering knuckles.
Click the anchors below to jump to product details and view available alloy grades, typical properties, and supply forms.
High-strength wrought ceramic aluminum matrix composites
Designed for aerospace and high-end equipment needing high strength, high stiffness, and low thermal expansion. Covers plates, extruded profiles, rings, and forgings, and supports T6/T651/T851 tempers. View the full knowledge article for detailed compositions, properties, and design guidelines.
- Achieve higher structural stiffness at the same mass, with steadier geometric control.
- Better consistency under thermal cycling and in assembly, with lower rework rates.
- Meets program material specs and batch consistency, enabling scalable adoption.
CT 7055 ceramic aluminum matrix composite
Ultimate tensile strength: 805 MPa
Yield strength: 750 MPa
Modulus of elasticity: 86 GPa
Elongation: 8%


CT2024 ceramic aluminum matrix composite
Ultimate tensile strength: 610 MPa
Yield strength: 451 MPa
Modulus of elasticity: 83.2 GPa
Elongation: 6.2%
-
ST051 (2xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 500–550 MPa
Yield strength: 460–490 MPa
Elastic modulus: 75–80 GPa
Elongation: 8–10%
Density: 2.88
Process conditions: continuous casting and rolling (T8)
-
ST012 (2xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 500–550 MPa
Yield strength: 380–480 MPa
Elastic modulus: 75–80 GPa
Elongation: 8–15%
Density: 2.86
Process conditions: continuous casting and rolling (T3)
-
LM041 (5xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 370–400 MPa
Yield strength: 280–300 MPa
Elastic modulus: 72 GPa
Elongation: ≥7%
Density: 2.70
Process conditions: continuous casting and rolling (partial anneal)
-
LM032 (6xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 300–320 MPa
Yield strength: 270–290 MPa
Elastic modulus: 70 GPa
Elongation: ≥6%
Density: 2.73
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion (T6)
-
LM052 (6xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 340–360 MPa
Yield strength: 320–340 MPa
Elastic modulus: 71 GPa
Elongation: ≥8%
Density: 2.74
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion (T6)
-
LM062 (6xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: ≥400 MPa
Yield strength: ≥330 MPa
Elongation: ≥10%
Density: 2.82
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion/forging (T6)
-
LM044 (7xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: ≥610 MPa
Yield strength: ≥570 MPa
Elongation: ≥10%
Density: 2.82
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion (T6)
-
LM021 (7xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 630–650 MPa
Yield strength: 570–590 MPa
Elastic modulus: 75–80 GPa
Elongation: 7–9%
Density: 2.86
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion (T6)
-
LM043 (7xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 650–720 MPa
Yield strength: 590–650 MPa
Elastic modulus: 76–85 GPa
Elongation: 7–14%
Density: 2.88
Process conditions: powder metallurgy extrusion (T6)
-
LM042 (7xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 680–720 MPa
Yield strength: 630–680 MPa
Elastic modulus: 75–80 GPa
Elongation: 7–9%
Density: 2.88
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion (T6)
-
LM032 (7xxx aluminum alloy)
Tensile strength: 700–750 MPa
Yield strength: 650–670 MPa
Elastic modulus: 75–80 GPa
Elongation: 4–7%
Density: 2.93
Process conditions: continuous casting and extrusion (T6)
Real application cases:
Deployed on the C919 program and moving into batch production. Reports show the first installation used 62 parts across load-bearing and dimension-critical components.
Examples: cargo floor panels, keel beams, APU intake door frames.
| Test item | CA7075-3.5 | 2196-T8511 | Improvement |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 579 | 476 | 21.6% |
| Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) | 634 | 524 | 21.0% |
| Elongation (%) | 7.4 | 6 | 23.3% |

Main load-bearing through beam

Load-bearing longeron

Fuel tank
If you are considering ceramic aluminum matrix composites for your project, email our team with your drawings and target specs. We will reply with a material and process proposal plus quotation.
High-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites
For China V/VI and above, and high boost/high BMEP platforms. It solves the limits of conventional high-temperature aluminum alloys on strength, thermal fatigue, wear, and corrosion at elevated temperatures. Learn more about high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites in the full knowledge article.
- Higher high-temperature tensile strength and thermal fatigue resistance. Suppress hot cracking and low-cycle fatigue.
- Better wear and corrosion resistance. Stable mating surfaces. Longer service life.
- System gains: lower friction/fuel/emissions, improved NVH.
Heat-resistant high-stiffness ceramic aluminum matrix composite (JG109X)
Tensile strength at 300 ℃: 150–170 MPa
Tensile strength at 350 ℃: 90–110 MPa
Room-temperature hardness: 120–140 HB

Heat-resistant high-strength ceramic aluminum matrix composite (JG201)
Tensile strength at 25 ℃: 550 MPa
Tensile strength at 300 ℃: 230 MPa
High-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composite (HD021)
Tensile strength at 250 ℃: 185–210 MPa
Tensile strength at 300 ℃: 140–160 MPa
Yield strength at 250 ℃: 160–180 MPa
Yield strength at 300 ℃: 120–135 MPa

Real application cases:
To meet China V/VI and above emissions rules, engine specific power keeps rising. Bench and on-road durability standards are stricter.
Conventional high-temperature aluminum alloys struggle to balance strength, wear, thermal fatigue, and corrosion. They also find it hard to keep stable life and low friction under high boost, high rpm, and high torque.
Our high-temperature nano-ceramic aluminum matrix composites use in-situ nano-ceramic dispersion strengthening. They outperform conventional high-temperature aluminum alloys in high-temperature tensile strength, thermal fatigue, corrosion resistance, and wear.
Contact us now
If you are evaluating high-temperature ceramic aluminum matrix composites for engines or other thermal-cycling parts, send us your drawings and duty conditions. We will provide a material and process proposal, with quotation and lead time, within 48 hours.
Casting ceramic aluminum matrix composites
Used for subframes, steering knuckles, control arms, and other complex integrated structures. Meets strength, fatigue, stiffness, and geometric control requirements while enabling "cast-to-replace-forging". See the full article on cast ceramic aluminum matrix composites .
- Significant weight reduction and one-piece forming. Machining and assembly cost less.
- Better batch consistency and system cost. Fit for platform-wide adoption.
- Flexible supply: alloy system and ceramic volume fraction can match targets.
Casting high-strength (JZ101) ceramic aluminum matrix composite
Ultimate tensile strength: 410–420 MPa
Yield strength: 340–350 MPa
Elastic modulus: 85–95 GPa


Casting high-modulus (JZ109) ceramic aluminum matrix composite
Ultimate tensile strength: 360–370 MPa
Yield strength: 320–330 MPa
Elastic modulus: >90 GPa
Casting high-ductility (JZ110) ceramic aluminum matrix composite
Ultimate tensile strength: 350 MPa
Yield strength: 290 MPa
Elongation: 14%
Fatigue limit: 110 MPa

-
FC011 (casting series)
Tensile strength: 330–350 MPa
Yield strength: 280–300 MPa
Elastic modulus: 71–73 GPa
Elongation: 10–14%
Density: 2.72
Process conditions: low-pressure casting (T6)
-
FC031 (casting series)
Tensile strength: 380–400 MPa
Yield strength: 300–320 MPa
Elastic modulus: 80–85 GPa
Elongation: 2–3%
Density: 2.77
Process conditions: low-pressure casting (T6)
-
FC021 (casting series)
Tensile strength: 360–370 MPa
Yield strength: 320–330 MPa
Elastic modulus: 90–95 GPa
Elongation: 0.5–1%
Density: 2.82
Process conditions: low-pressure casting (T6)
-
FC041 (casting series)
Tensile strength: 530–550 MPa
Yield strength: 450–470 MPa
Elastic modulus: 78–80 GPa
Elongation: 3–4%
Density: 2.89
Process conditions: low-pressure casting (T6)
-
FC052S (casting series)
Tensile strength: 365–410 MPa
Yield strength: 290–350 MPa
Elastic modulus: 72–75 GPa
Elongation: 5–20%
Density: 2.72
Process conditions: squeeze casting (T6)
-
FC071S (casting series)
Tensile strength: 400–460 MPa
Yield strength: 340–380 MPa
Elastic modulus: 72–75 GPa
Elongation: 2–5%
Density: 2.69
Process conditions: squeeze casting (T6)
-
FC081 (casting series)
Tensile strength: ≥630 MPa
Yield strength: ≥600 MPa
Elongation: ≥4%
Density: 2.85
Process conditions: casting (T6)
-
FC082 (casting series)
Tensile strength: 540–560 MPa
Yield strength: 460–490 MPa
Elongation: 7–15%
Process conditions: squeeze casting (T6)
-
FC061HTF (casting series)
Tensile strength: 185–210 MPa
Yield strength: 140–150 MPa
Elongation: 10–12%
Process conditions: die casting, no heat treatment
Real application cases:
Casting Al-MMC steering knuckle
56% lighter than cast iron knuckles.
Casting enables integrated complex structures.
Contact us now
- Cast to replace forging: meets knuckle strength/fatigue and geometric tolerances. Casting reduces machining and assembly complexity.
- Significant weight reduction: lower unsprung mass improves handling and NVH, with better braking and energy use.
- Cost and consistency: integrated complex structures cut system cost and improve batch consistency.
| Material process | QT450 cast knuckle | 6082 forged knuckle | Al-MMC cast knuckle |
| Yield strength | 310 MPa | 280 MPa | 290 MPa |
| Elongation | 9%-11% | 10%-11% | 10%-14% |
| Density | 7.1 g/cm³ | 2.71 g/cm³ | 2.71 g/cm³ |
If you are considering casting ceramic aluminum matrix composites for subframes, steering knuckles, control arms or other integrated chassis parts, email us your drawings and target specs (loads, stiffness, weight, CTE, life). Our engineering team will respond with a material and casting proposal plus quotation.
Ceramic aluminum matrix composite powders
High-sphericity, low-satellite, narrow PSD powders for LPBF/SLM. Stable laser absorption and melt pool behavior, enabling one-piece forming of complex internal channels and lattices. Learn more about ceramic aluminum matrix composite powders in the full knowledge article.
- Easier near-net shaping: good powder flow, stable layer thickness, fewer pores and spatter.
- Dimensional and thermal-cycle stability: low expansion + high modulus, minimal thermal distortion.
- Compatible with mainstream machines and batch-consistency control for scalable production.
-
FCA101X-1 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 400–480 MPa
Yield strength: 260–370 MPa
Elongation: ≥10%
Modulus of elasticity: 70 GPa
-
FCA101X-2 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 450–530 MPa
Yield strength: 310–410 MPa
Elongation: ≥7%
Modulus of elasticity: 72 GPa
-
FCA101X-11 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 460–540 MPa
Yield strength: 320–430 MPa
Elongation: ≥5%
Modulus of elasticity: 75 GPa
-
FCA101X-10 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 470–550 MPa
Yield strength: 330–440 MPa
Elongation: ≥3%
Modulus of elasticity: 80 GPa
-
FCA101Y-1 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 420–480 MPa
Yield strength: 290–360 MPa
Elongation: ≥8%
Modulus of elasticity: 72 GPa
-
FCA101Y-2 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 460–520 MPa
Yield strength: 300–370 MPa
Elongation: ≥6%
Modulus of elasticity: 74 GPa
-
FCA101Y-6 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 480–540 MPa
Yield strength: 310–380 MPa
Elongation: ≥4%
Modulus of elasticity: 78 GPa
-
FCA101Y-7 (powder series)
Tensile strength: 500–560 MPa
Yield strength: 320–390 MPa
Elongation: ≥3%
Modulus of elasticity: 82 GPa
- Easier near-net shaping: high sphericity, low satellites, narrow PSD. Stable spreading and forming. Less spatter and porosity.
- Structural stiffness and dimensional stability: in-situ nano-ceramic reinforcement. Higher modulus, lower thermal expansion. Tighter geometry control under thermal cycling.
- Compatible with mainstream LPBF machines: process proven on BLT-S500 (Bright Laser Technologies, China). Migrates to peer platforms.
- Typical applications: aerospace mechanisms, thermal-cycling parts, precision load-bearing joints, lightweight brackets, and more.
Real application cases:
Hinge arms are critical load-bearing connectors on the airframe. They demand high strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability, while balancing lightweight and consistency under thermal cycling.
Conventional cast/forge + machining struggles to balance weight and assembly accuracy. Additive manufacturing (LPBF) forms complex topology in one build and shortens delivery.
C919 door hinge arm
Overall size: 450 × 350 × 600 mm
Powder grade: FCA101Y-6 (ceramic aluminum matrix composite powder)
Machine: BLT-S500 (Bright Laser Technologies, China)

- Ultimate tensile strength: > 500 MPa
- Yield strength: > 300 MPa
- Elongation: > 6%
We offer integrated material-structure-process solutions (plate/profile/forging/casting/LPBF).
We support fast onboarding and batch consistency control, and provide the process window and quotation within 48 hours.
If you are evaluating ceramic aluminum matrix composite powders for LPBF/SLM, send us your 3D models, build envelope and target properties (strength, stiffness, CTE, life, weight). Our team can suggest suitable powder grades, process windows and an estimated quotation.
Advantages of ceramic aluminum matrix composites
- Low density: keeps the lightweight DNA of aluminum. System-level weight cuts benefit both sprung and unsprung mass.
- High strength: ultimate tensile strength can exceed 800 MPa. Higher specific strength than Ti alloys for "lighter yet stronger."
- High stiffness: modulus up to ≈95 GPa. Higher specific stiffness than Ti alloys; thin walls and long cantilevers resist deformation.
- Fatigue resistance: representative comparisons—rotating bending fatigue ≈94% higher than 7xxx Al; ≈87% higher than 2xxx Al; axial double open-hole fatigue ≈30% higher than Al-Li 2060.
- Wear resistance: higher hardness and lower mass loss. Grooves and mating surfaces retain fit better.
- Corrosion resistance: inherits aluminum's anti-corrosion advantage. Fits multiple service media and coating systems.
- High-temperature capability: markedly higher high-temp strength and creep resistance. Strong thermal-fatigue resistance for high boost and frequent thermal cycling.
- Easy to process/integrate: friendly to casting and plastic deformation. Compatible with machining and welding. Complex structures can be integrated; assembly is steadier and cheaper.
Chalco offers customized solutions for ceramic aluminum matrix composites
Use lighter materials to achieve stronger, more stable, and more cost-efficient structures. We provide integrated "material-structure-process-quality” customization around your targets and duty conditions.
Four dimensions of customization
Set quantitative goals and test standards for strength/stiffness, fatigue life, CTE (thermal expansion), thermal conductivity/dissipation, wear/corrosion, working temperature range, and life curve. Design formulas and process windows backward from targets to ensure verifiable, scalable results.
Offer 2xxx/6xxx/7xxx systems (including high-temperature and high-strength wrought families) with tempers such as T6/T651/T851. Balance strength, CTE, manufacturability/weldability, and cost.
Use in-situ nano-ceramics. Precisely tune volume fraction, particle size (nano–micron), morphology, and spatial distribution (uniform/local/graded) to hit key metrics like strength, CTE, and thermal conductivity.
Provide wrought (extrusion/rolling/forging/ring rolling), casting (low-pressure/squeeze/infiltration), and additive powders (LPBF/SLM). Pair with stress relief/HIP/aging plus machining/surface engineering to balance complexity, batch consistency, and total cost.
Application solutions
- High-strength wrought (plate/profile/forging): in-situ reinforcement + deformation processing for extreme strength and dimensional stability in aerospace and high-end structures.
- High-temperature (engine/thermal-cycling parts): co-optimize high-temperature strength, creep, and thermal-fatigue resistance for pistons/cylinder heads/hot-end parts.
- Cast-to-replace-forging (chassis/integrated structures): low-pressure/squeeze casting and infiltration. Fewer parts, higher yield, lower total cost.
- Additive powder (LPBF/SLM): high sphericity/low satellites and stable process windows. Support complex topology and fast small-batch onboarding.
Our ceramic aluminum matrix composite partners
We collaborate with many industry leaders to develop and apply high-performance ceramic aluminum matrix composites. Our key partners include:
- CRRC: a global leader in rail transit equipment.
- AVIC: a core force in China's aviation industry. Joint development of aircraft materials and parts.
- CASIC: applications in space equipment.
- China Ordnance: applications in weapons systems and defense projects.
- Norinco Group: supports lightweighting and durability in weapon equipment.
- COMAC: China's main civil aircraft developer. Applied in programs such as C919.
- AECC: a pioneer in aero-engine R&D and manufacturing. Broad use in engines and other critical parts.
Forming processes of ceramic aluminum matrix composites
Deformation processing (extrusion/rolling/forging/ring rolling)
Start from cast ingots to achieve isotropy and refined microstructure. Get plates/profiles/forgings with high strength, long fatigue life, and stable geometry.
Control homogenization, deformation paths, and recrystallization. Use stress relief/stretch straightening/HIP to reduce distortion and scatter.
Squeeze casting/pressure infiltration
Force molten aluminum to fill the die or infiltrate a preform under high pressure. Low porosity and high mechanical properties suit load-bearing frames and sections with large wall changes.
Tightly control the pressure–time curve and die thermal management. Verify preform strength/porosity/coating to suppress brittle interfacial phases.
Vacuum/pressure infiltration
First make a shaped ceramic preform. Then use vacuum or gas/liquid pressure to infiltrate aluminum, enabling high volume fraction, directional reinforcement, and high stiffness.
Watch preform connectivity and pore-size distribution, driving force and dwell time. Avoid uninfiltrated zones/entrapped gas and overreaction at the interface.
Stirring/compound stirring
Disperse ceramic particles such as SiC/Al₂O₃/TiB₂ into molten aluminum or semi-solid slurry. Then low-pressure/gravity/die cast directly. Good for integrated, cost-sensitive, mass parts.
Focus on wetting and dispersion: control temperature window, Mg content/fluxes, ultrasonic/electromagnetic stirring, and degassing to prevent agglomeration and porosity.
Additive manufacturing
Print complex topology and internal channels directly. Ideal for fast iteration, small batches, and brackets/frames needing thermal-cycle stability.
Check powder sphericity/oxygen/moisture and scanning strategy. Pair with stress relief/HIP/aging and machining datums to control warpage and residual stress.
Powder metallurgy
Suited to nano-scale uniformity, high/special volume fractions, and small cross-sections with high specs. Composition and particle distribution are precisely controlled.
Densification and oxygen control are key: often combine HIP/SPS with secondary deformation. Size is limited and cost is sensitive to batch scale.
In-situ reaction reinforcement
Generate fine ceramics (e.g., TiB₂/TiC) within the aluminum matrix in situ. Clean interfaces, good wetting, and strong bonding enable high strength and high fatigue resistance in wrought products.
Strictly control exothermic reactions and brittle phase formation. Stabilize particle size/distribution. Raw material purity and alloying elements (e.g., Mg) are also critical.
What we can provide
- Fast evaluation (48 h): based on 3D model + duty, deliver material/process feasibility, process window, and quote/lead time.
- Material selection and formula customization: match in-situ nano-ceramic volume fraction/size/distribution with 2xxx/6xxx/7xxx matrices to hit strength/CTE/temperature/thermal targets.
- DFM/DFA co-design: optimize fillets, wall thickness, rib layout, parting/support strategy. Output manufacturable drawings with tolerance advice.
- "Cast-to-replace-forging" and cost optimization: low-pressure/squeeze casting and infiltration to cut machining and part count, reducing cost and lead time.
- Process route implementation: wrought (extrusion/rolling/forging/ring rolling + T6/T651/T851), additive (LPBF + stress relief/HIP/aging), casting (LPDC/squeeze/infiltration).
- Machining and fixturing package: PCD tool parameters, clamping/vacuum fixtures, machining allowances, and tolerance stack-up.
- Surface and corrosion systems: hard anodizing/MAO/coatings and galvanic isolation design, matched to media and life requirements.
- Validation and quality control: material/bench/road tests, CT/X-ray, CMM, QCP/SPC, support for PPAP/FAI documentation.
- Prototypes → small batch → mass production: batch consistency and Cpk control, supply chain and delivery coordination.
- Failure diagnosis and continuous improvement: on-site technical support and FA. Ongoing weight/cost reduction and life extension.
Integrated manufacturing and R&D capability
Strength/capacity
Four production lines for in-situ synthesis, special casting, semi-continuous casting, and additive powders. Annual output: 18,000 tons of ceramic aluminum alloys and products. Integrated delivery from materials to finished parts.
Equipment/hardware
100+ core machines, including reaction synthesis furnaces, counter-gravity casting systems, and large-format metal SLM printers.
20+ test instruments such as optical emission spectrometers and image analyzers. Full-process traceability.
Experience/team
Since 1992, we have focused on nano-ceramic alloy research and industrialization. We cover alloy design, process development, and mass manufacturing.
Research/credentials
Backed by domestic universities and institutes. Team includes 1 Changjiang Scholar, 1 professor, 4 associate professors, and 20+ masters/PhDs.
Holds 7 invention patents. We continuously deliver verifiable material and process solutions.




Inspection and quality assurance
- Fluorescent penetrant inspection equipment
- X-ray machine (real-time imaging system)
- Fatigue testing machine
- Tensile testing machine
- Hydrogen analyzer
- Oxygen/nitrogen/hydrogen analyzer
- Microscope
- X-ray diffractometer
- Particle size analyzer
- Optical emission spectrometer

We also supply related aluminum alloy products
We provide plates, profiles, forgings, and rings.
We support composition/temper selection, machining and heat-treat coordination, and compliant test reports.
If you need specific targets (strength/fatigue/CTE/temperature range), leave a message. We will return a plan and quotation within 48 hours.
High-strength aluminum alloys
-
7075 aluminum alloy
A high-strength aluminum alloy for aircraft structures. Poor weldability and lower corrosion resistance.
-
2024 aluminum alloy
Good fatigue performance and high strength. Widely used in aircraft structures.
-
2219 aluminum alloy
A high-strength alloy for spacecraft structures. Offers good weldability.
-
7050 aluminum alloy
High resistance to stress corrosion. Used in aerospace structures.
-
7068 aluminum alloy
One of the strongest commercial aluminum alloys. Used in aerospace and automotive.
-
5083 aluminum alloy
Excellent corrosion resistance and weldability. Suited to marine and chemical equipment.
High-temperature and wear-resistant aluminum alloys
-
2618 / 2618A aluminum alloy
Typically used for forged pistons/connecting rods/turbine parts. Keeps strength and fatigue advantages at 200–250 °C for long periods.
-
2219 aluminum alloy
Common for space tanks and welded structures. Good weldability. Retains strength at 150–200 °C, better than typical 6xxx/7xxx alloys in this range.
-
2014 / 2024 aluminum alloy
Hold properties well at 125–150 °C compared with 6xxx/7xxx alloys.Fit medium-temperature load-bearing structures.
Samples & Fast Quote
Custom materials tailored to your target CTE, temperature range and thermal conductivity – send us your drawings and operating conditions, and within 48 hours we will provide a material solution, process window, quotation and lead time.
Related questions (FAQ)
What is an aluminum matrix composite?
An engineering material with aluminum/aluminum alloy as the matrix and ceramic reinforcements such as SiC, TiB₂, or Al₂O₃.
It aims to keep low density while boosting strength, stiffness, wear, thermal, and dimensional stability.
How strong is a ceramic aluminum matrix composite?
It depends on reinforcement type/volume fraction and process route.
Casting grades typically reach YS 250–350 MPa and UTS 300–450 MPa.
In-situ reinforced wrought grades go higher, with UTS 700–800 MPa (grade and temper specific).
If you have target metrics (strength/CTE/temperature/thermal), we can tailor composition and process.
Are aluminum and ceramics the same?
No. Aluminum is a metal with good thermal/electrical conductivity and high ductility.
Ceramics are non-metals with high hardness, low thermal expansion, and wear/heat resistance but higher brittleness.
Combining them delivers lightweight parts with higher strength/stiffness and better thermal-cycle stability.
What are the advantages vs. Al-Li and titanium alloys?
Specific strength/stiffness can match or exceed titanium, with more controllable cost.
Compared with Al-Li, CTE is lower and wear resistance is better, improving assembly consistency.